Use context: kubectl config use-context k8s-c2-AC
Write a command into /opt/course/15/cluster_events.sh which shows the latest events in the whole cluster, ordered by time (metadata.creationTimestamp). Use kubectl for it.
Now kill the kube-proxy Pod running on node cluster2-node1 and write the events this caused into /opt/course/15/pod_kill.log .
Finally kill the containerd container of the kube-proxy Pod on node cluster2-node1 and write the events into /opt/course/15/container_kill.log .
Do you notice differences in the events both actions caused?
译文:
在 /opt/course/15/cluster_events.sh 中写一条命令,显示整个集群的最新事件,按时间(metadata.creationTimestamp)排序。使用 kubectl 来实现。
现在,杀死运行在cluster2-node1节点上的kube-proxy Pod,并将其引起的事件写入 /opt/course/15/pod_kill.log 中。
最后,杀死cluster2-node1节点上的kube-proxy Pod的containerd容器,并将事件写入 /opt/course/15/container_kill.log 中。
你是否注意到这两个动作引起的事件的不同?
解答:
kubectl config use-context k8s-c2-ACsh 脚本
echo "kubectl get events -A --sort-by=.metadata.creationTimestamp" > /opt/course/15/cluster_events.sh查找proxy pod ,并kill node1上面的pod,然后检查日志
k -n kube-system get pod -o wide | grep proxy
k -n kube-system delete pod kube-proxy-
sh /opt/course/15/cluster_events.sh > /opt/course/15/pod_kill.log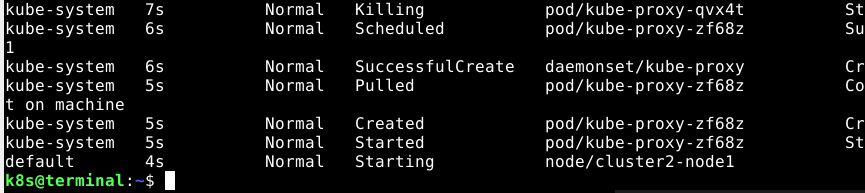
连接到node1并结束掉proxy 容器
ssh cluster2-node1
root@cluster2-node1:~# crictl ps | grep kube-proxy
root@cluster2-node1:~# crictl stop 254ceb6e415ac
root@cluster2-node1:~# crictl ps | grep kube-proxy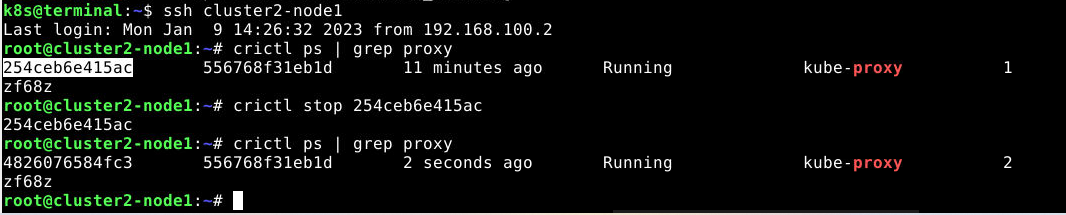 写日志
写日志
sh /opt/course/15/cluster_events.sh > /opt/course/15/container_kill.log